How to Identify and Treat Stevens-Johnson Syndrome?
Advertisement
Many people are affected by Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) nowadays. It is a rare and serious condition that affects the skin and mucous membranes. It often begins with flu-like symptoms, such as fever and sore throat, followed by a painful rash that spreads and blisters. It happens in relatively less time because of the immune system's rapid response. SJS need to be treated immediately. Otherwise, it can cause serious complications. In this article, we will discuss in detail what Stevens-Johnson Syndrome is and what the symptoms of this syndrome are.
What is Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) is a severe condition which impacts the skin and mucous membranes. It is a hypersensitivity reaction that happens when medications or infections trigger the immune system. After some days, a painful rash occurs, followed by blisters.
This condition can affect various body parts, including the mouth, eyes, and genitals. This leads to painful sores, which cause difficulty in eating and drinking. SJS is considered a medical emergency and usually requires hospitalization for treatment. Recovery can take weeks to months, depending on the severity of the condition. In severe cases, SJS can lead to life-threatening complications like dehydration, infections, or organ failure.
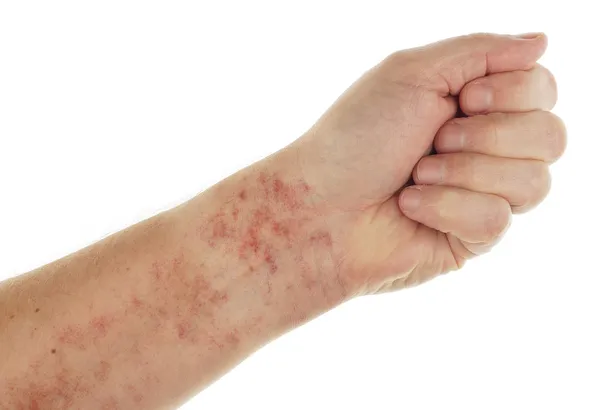
Symptoms of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) develops in very little time. The condition starts with flu-like signs, such as cough, sore throat, joint pain and fatigue. These symptoms last for 1 to 3 days. Then, a red or purple rash may appear on the upper body and spread to other parts. This rash often becomes lesions with a dark center. In severe cases, the skin may peel and cause discomfort.
The mucous membranes are also commonly affected. Painful blisters and sores can appear in the mouth and throat. It makes swallowing difficult and eating or drinking painful. The eyes may become red, watery, and irritated. Blisters can also form in the genital area, causing pain during urination. Other symptoms include swelling in the lips, tongue, or face and skin shedding. SJS is a medical emergency. If these symptoms occur, particularly after starting a new medication or following an infection, seek immediate medical attention.
Causes of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS)
There are several causes of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome. Some of them are explained below:
Medications
The most frequent cause of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome is an adverse reaction to certain medications. Nearly any drug can trigger SJS, but some types are more often involved. Antibiotics, particularly sulfa drugs and penicillins, are well-known antibiotics that cause this syndrome. Anticonvulsants, such as carbamazepine and lamotrigine, are also linked to the condition. Common pain relievers like acetaminophen and ibuprofen can sometimes cause SJS as well.
Infections
Infections, especially viral ones, can also lead to Stevens-Johnson Syndrome. Common viral infections that may trigger SJS include the herpes simplex virus, Epstein-Barr virus, influenza, and mumps.
Genetic factors
Genetic factors serve a major role in the development of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome. Some people have variations in the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) gene. It increases the risk of developing SJS when there is exposure to specific drugs. This genetic predisposition can make some people more susceptible to the condition.
Other Factors
People with weak immune systems are at greater risk of having the SJS. Moreover, if a person has Steven-Johnson Syndrome and again has that triggering medicine, it could increase the risk of recurrence.
Risk factors for Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) has multiple risk factors. Here are the main risk factors:
- People over 60 years
- People with compromised immune system
- People with chronic diseases
- People with a previous history of SJS
- Genetic factors
- Certain medications
How Your Immune System Affects Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
The immune system plays the main role in the development and progression of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS). This condition is primarily classified as a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's cells. T-cells, especially CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes, become activated in response to triggers like medications or infections.
These T-cells target skin cells (keratinocytes), causing tissue damage and blistering. The process involves substances like perforin and granzyme B, which T-cells release. Perforin creates pores in keratinocyte membranes, which is why granzyme B enters and induces cell death through apoptosis. Inflammatory mediators like cytokines also take part in the progression of SJS. Cytokines such as tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interferon-gamma increase skin damage.

How long it takes to recover from Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
It usually depends on the severity of the condition and overall health. In moderate cases, it usually takes about 2 to 4 weeks as the skin and mucous membrane regenerate. However, in severe cases with extensive skin damage or complications like infections or eye problems, recovery can take several weeks to a few months. However, in severe cases, it takes several weeks to a few months because of extensive skin damage and complications. After recovery, some individuals may experience long-term effects, such as scarring, eye issues, or heightened skin sensitivity, which may need ongoing management and care.
How much it takes time to develop this syndrome
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) usually begins within 1 to 3 weeks after exposure to a triggering medication or infection. The process usually begins with a prodromal phase. In this phase, individuals experience flu-like symptoms, including fever, sore throat, and fatigue. It lasts from 1 to 3 days. After this, a rash generally appears within a few days to a month after starting a medication. For most drugs, symptoms can show up as early as 1 week, but for some medications like anticonvulsants, it may take up to 2 months for symptoms to appear. After this, it can spread quickly, reaching its peak within 4 days.
Note: You should immediately consult your doctor for specialized and prompt treatment.
Conclusion
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) is a rare but serious condition that needs quick treatment. The main causes of developing this syndrome are medication and infection, but some people may be more at risk due to their genetics or health. If you or someone you know has flu-like symptoms, it becomes a painful rash. Then, it’s important to get medical help right away. Stay informed and stay safe!
On this page
What is Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Symptoms of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Causes of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) Medications Infections Genetic factors Other Factors Risk factors for Stevens-Johnson Syndrome How Your Immune System Affects Stevens-Johnson Syndrome How long it takes to recover from Stevens-Johnson Syndrome How much it takes time to develop this syndrome ConclusionAdvertisement












